What is Enterprise Application Integration (EAI)
Today, businesses heavily rely on a variety of software programs to streamline operations, manage data, and spur growth. These applications, however, frequently work in isolation, resulting in fragmented data, ineffective procedures, and lost possibilities for collaboration. Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) is useful in this situation can be equated to assembling a complex puzzle. When putting together a puzzle, each piece contributes in a different way to the completed image. If the pieces are not connected correctly, the puzzle may look distorted. Similarly, several software programs in a business setting, each storing important information and functionality have their contributions. EAI fills in the blanks, acting like a master puzzle solver, ensuring that information flows freely between applications, that actions are synchronised, and that a comprehensive picture of effective and interrelated operations is shown.
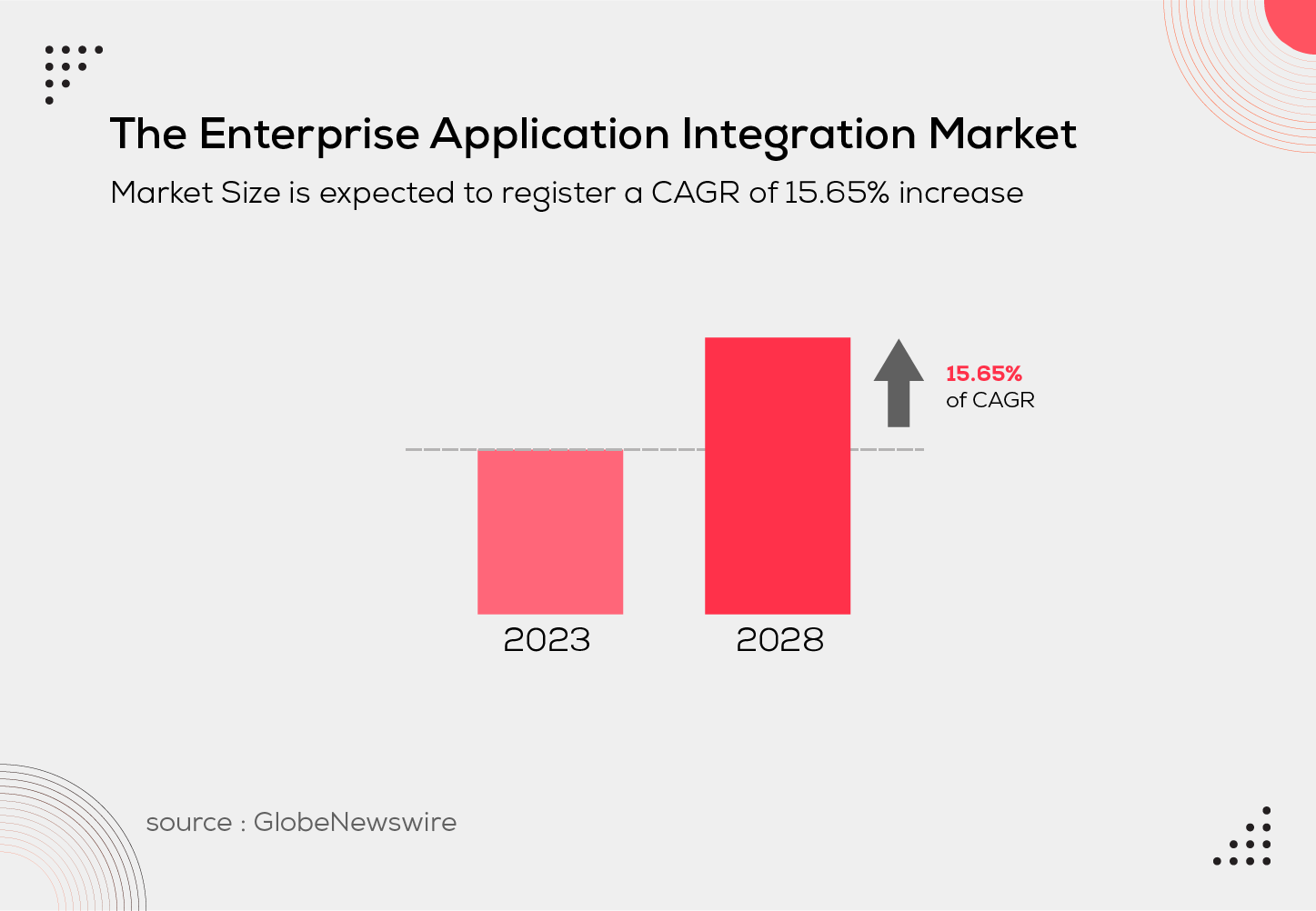
According to GlobeNewswire, the enterprise application integration market is expected to register a CAGR of 15.65% over the forecast period of 2023-2028.
In this article, we will explore the concept of Enterprise Application Integration, its significance in the digital era, and its advantages to businesses.
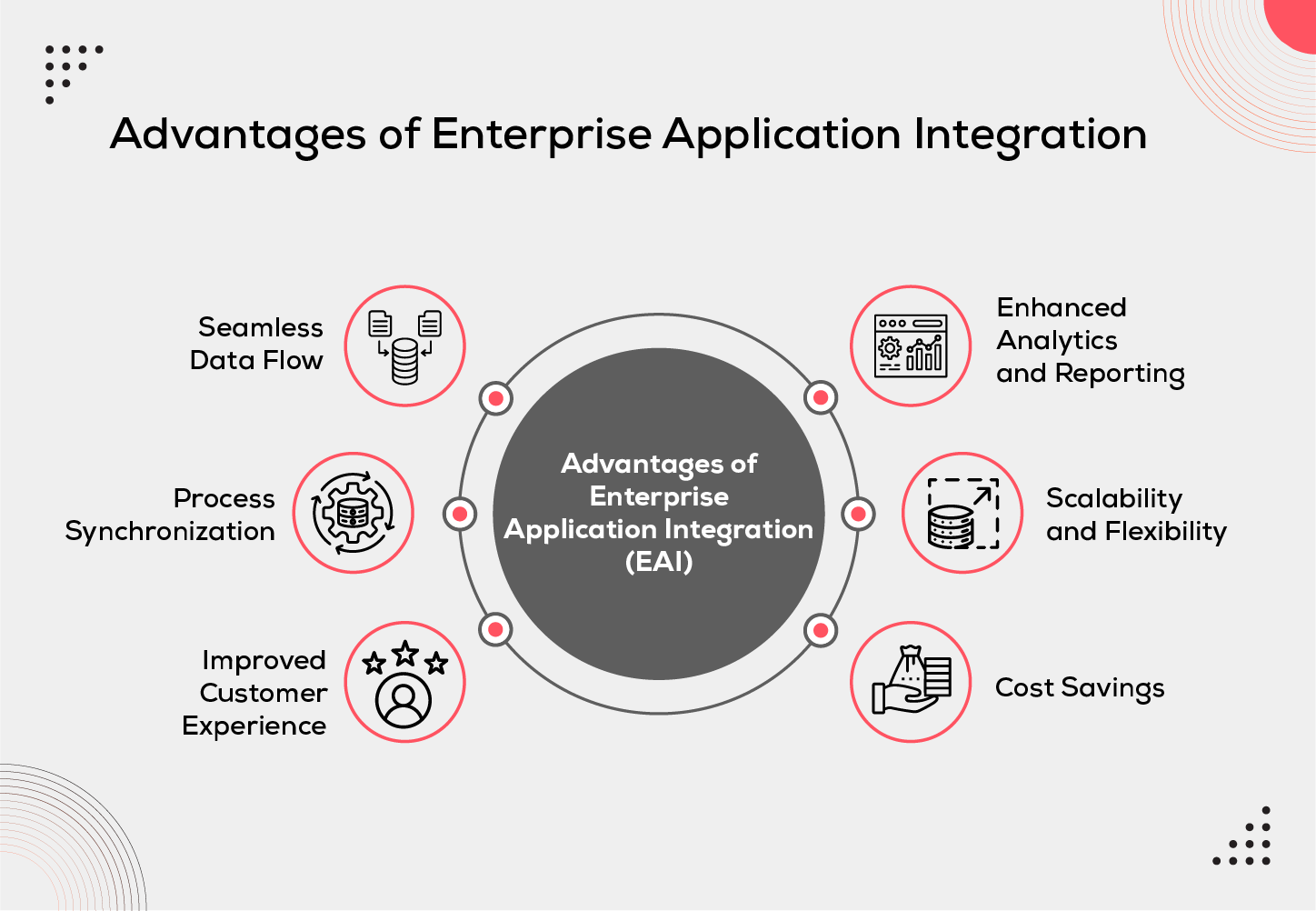
The Advantages of Enterprise Application Integration
Implementing Enterprise Application Integration offers numerous benefits to businesses. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
-
Seamless Data Flow:
Seamless Data Flow is a critical benefit of Enterprise Application Integration. EAI enables organizations to establish smooth and real-time data exchange among their various applications. This means that data can be seamlessly transferred between different systems, ensuring that accurate and up-to-date information is readily available across the entire organization. This integrated data can be utilized for in-depth analysis, forecasting, and trend identification, leading to better-informed decisions that drive business growth and efficiency.
-
Process Synchronization:
The process of synchronization ensures that data and information are consistently and accurately shared among different systems, improving the overall efficiency of business processes. For example, when a sales order is entered into a CRM system, EAI can automatically trigger actions in the ERP system to generate an invoice, update inventory levels, and initiate the fulfilment process. This seamless synchronization of processes eliminates delays, reduces manual efforts, and minimizes the risk of errors or miscommunications.
-
Improved Customer Experience:
This is a significant benefit of EAI. It enables organizations to integrate customer data from different systems and applications to gain a comprehensive view of their customers. This integrated data can be used to provide personalized experiences, such as targeted product recommendations, customized promotions, and efficient customer service. By delivering relevant and tailored experiences, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased revenue and growth for the organization.
-
Enhanced Analytics and Reporting:
EAI enables businesses to leverage advanced analytics tools to generate meaningful insights that drive informed decision-making and strategic planning. By gaining a deeper understanding of their operations and customers, organizations can make better decisions, optimize their processes, and stay ahead of the competition.
-
Scalability and Flexibility:
Technology evolves, and new applications emerge while the older applications become outdated. EAI allows organizations to scale and adapt their technology infrastructure more easily. By integrating new applications or retiring outdated ones, businesses can quickly respond to changing market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
-
Cost Savings:
EAI can help organizations reduce costs by automating manual tasks, streamlining processes, and improving overall efficiency. By reducing the time and resources needed to manage their systems, organizations can free up staff to focus on more strategic tasks, leading to additional cost savings and increased productivity.
The Need for EAI
In today's interconnected business world, organizations rely on a diverse range of applications to manage various operational aspects. Applications like Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Supply Chain Management (SCM), and Human Resources Management (HRM), among others, serve specific purposes and hold invaluable data. However, when these applications function in isolation and fail to communicate effectively with one another, it can pose various challenges. Here's where EAI comes into action, seamlessly integrating these applications for organizations to optimize their benefits and operations.
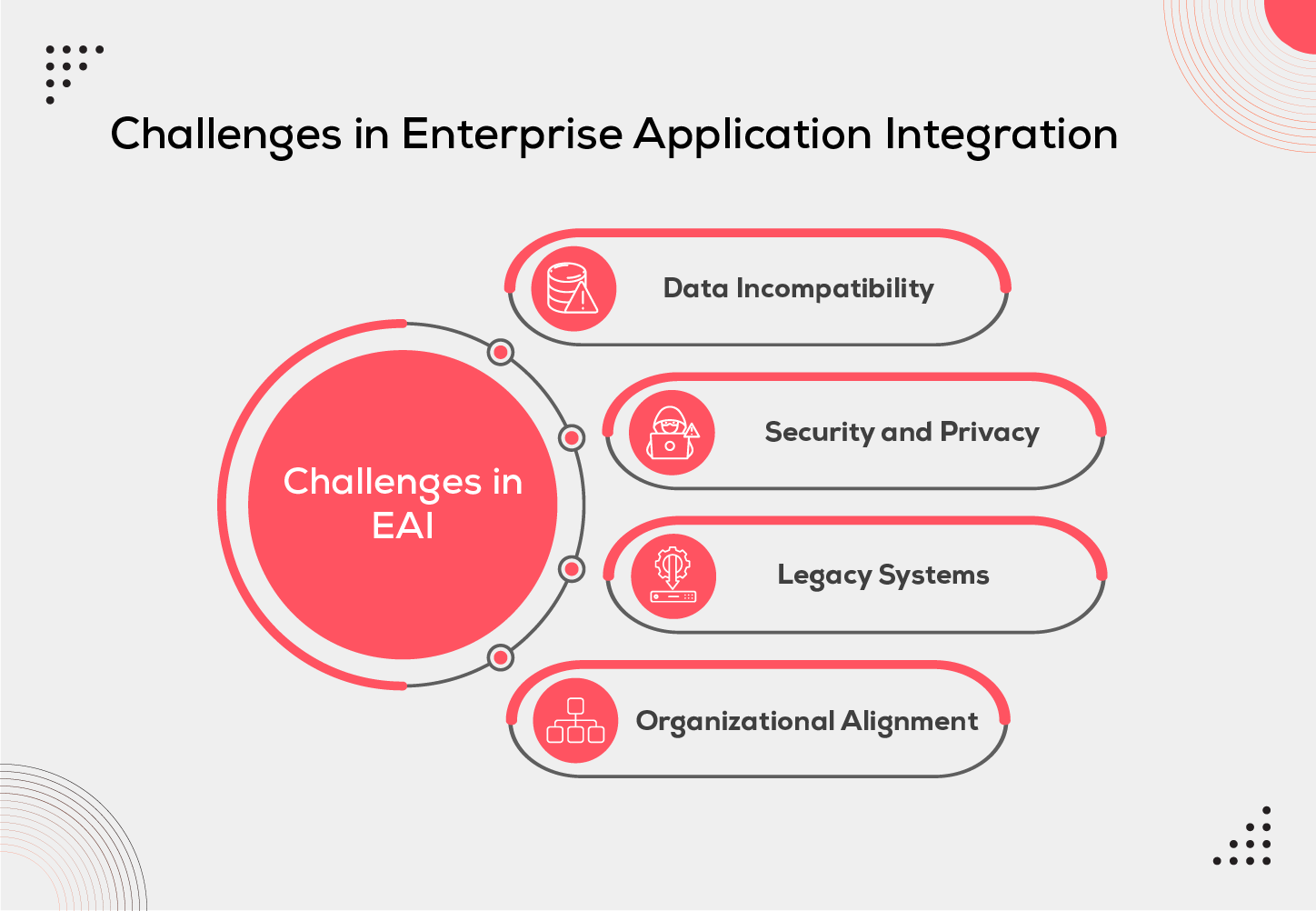
Overcoming Challenges in Enterprise Application Integration
Although EAI offers many benefits, organizations must address certain challenges. Here are some common ones:
-
Data Incompatibility:
Applications often utilise different data formats, structures, or standards, making seamless data transfer between them challenging. This creates a complex task during the integration process, which involves mapping and transforming data from one format to another. To ensure that data can be effectively exchanged between different applications, organizations need to implement robust data transformation mechanisms that can convert data from one format to another. Additionally, standardization efforts can help ensure that the data is consistent across different applications.
-
Security and Privacy:
When integrating applications, sensitive data is often shared between systems, which can raise security concerns. This sensitive data could include personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, or other confidential information. Secure data transmission protocols can ensure that data is transmitted securely between applications, protecting it from interception or tampering.
-
Legacy Systems:
Legacy systems may often use outdated technologies and may lack the necessary documentation or support, making it difficult to understand how the system works or troubleshoot issues that arise during integration. Organizations need to modernize or replace legacy systems to ensure smooth Enterprise Application Integration, enhancing operational efficiency.
"Stefan Van Der Zijden, VP Analyst at Gartner, notes “For many organisations, legacy systems are seen as holding back the business initiatives and business processes that rely on them. When a tipping point is reached, application leaders must look to application modernisation to help remove the obstacles.”
-
Organizational Alignment:
Implementing EAI solutions can bring about significant changes to an organization's existing processes and systems, which may result in resistance to change. To achieve a smooth integration and overcome this resistance, it is crucial to establish organizational alignment and a shared vision for the EAI project. This necessitates close collaboration and coordination among various departments and IT teams to ensure that everyone is working towards a common goal.
Commonly Integrated Applications:
On-premise:
On-premise integration means hosting and managing solutions within an organization's physical location. This approach allows for control, security, and customization over applications. It requires a significant initial investment and meticulous maintenance but provides enhanced flexibility and precise control over data and software. However, it may be less flexible and scalable compared to cloud-based alternatives.
SAAS:
SAAS has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its flexibility and scalability. This integration refers to the process of integrating different SaaS applications to work together seamlessly. These applications are cloud-based software applications and can be achieved through using a variety of integration methods, such as API integration, middleware integration, and custom integration that are accessed over the internet anywhere and anytime.
Application-to-Application:
Application-to-Application (A2A) integration refers to the process of integrating two or more software applications to work together seamlessly. A2A integration is typically used within an organization's internal IT environment, where multiple applications are used to support different business functions, such as finance, human resources, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Enterprise Application Integration Levels
1. Data Integration:
This level of integration allows for the sharing of information between applications with complete transparency, ensuring that integration is clear and complete.
2. Communications-Level Integration:
This level specifies how communication takes place between applications and ensures that they can communicate with each other. APIs are commonly used to accomplish this task.
3. Presentation-Level Integration:
This level combines multiple applications into a single one with a standard interface, which can be achieved through middleware solutions and technology.
4. Application Interface Integration:
This level involves integrating the interfaces of different applications to enable the sharing of data and functionality.
5. Business Process Integration:
This level involves automating processes to improve performance and achieve enterprise goals, and can be achieved through pull, push, or process trigger methods.
Approaches to Enterprise Application Integration
There are various approaches to implementing Enterprise Application Integration, each with its strengths and considerations. Let's explore all the approaches:
-
Point-to-Point Integration
This approach involves connecting two or more systems directly, typically through a custom interface or middleware. In this approach, each system is connected directly to the other systems it needs to communicate with, creating a "spaghetti" network of connections. While this approach can be effective in connecting two or three systems, it can become bulky and problematic to manage when the number of systems increases.
-
Hub and Spoke Integration
In a hub-and-spoke integration, each system is connected to the hub, which acts as a central point for data exchange and communication. The hub manages the flow of data between the different systems, ensuring that each system receives the data it needs in the correct format and at the appropriate time. This approach is also known as "hub-and-spoke" or "hub-and-spoke architecture."
-
Middleware
Middleware is a software layer that sits between different applications, systems, and databases to enable communication and data exchange. It provides a range of services, such as data transformation, message queuing, security, and transaction management. Additionally, it offers a centralized platform for managing and monitoring communication between different systems and applications.
-
Microservices
One of the key benefits of microservices is that it enables organizations to break down complex applications into smaller, more manageable services. This allows developers to focus on specific areas of the application, improving agility, and reducing the risk of errors or bugs.
-
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA)
With SOA, organizations can easily create complex software systems by combining and reusing existing services, leading to a flexible and scalable EAI approach. Consequently, businesses can quickly respond to changing business requirements and integrate new systems or applications as needed.
-
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
An ESB is a software architecture that provides a centralized platform for integrating different systems and applications. It serves as a middleware layer that enables communication between different systems and applications by facilitating message routing, transformation, and translation.
Best Practices for Successful Enterprise Application Integration
Here are some best practices for a successful Enterprise Application Integration that organizations should consider:
-
Define Clear Business Objectives:
Before embarking on an EAI project, it is important to define the business objectives and goals that the project aims to achieve. This can help to ensure that the project is aligned with the organization's strategic priorities and that the benefits of EAI are clearly understood by all stakeholders.
-
Establish Governance and Ownership:
EAI projects should have clear governance and ownership structures in place to ensure that the project is managed effectively and efficiently. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication channels, and developing processes for decision-making and issue resolution.
-
Use Standard Integration Patterns:
Standard integration patterns, such as publish-subscribe, request-response, and data synchronization, can help to simplify EAI projects and reduce complexity. Using standard patterns can also make it easier to troubleshoot issues and maintain the integration over time.
-
Implement Robust Security Measures:
EAI projects involve the sharing of sensitive data between applications, which can make security a critical concern. Implementing robust security measures, such as access controls, encryption, and secure data transmission protocols, is crucial to protect data integrity and confidentiality.
-
Monitor and Measure Performance:
EAI projects should be monitored and measured to ensure that they are meeting the defined business objectives and performance targets. This can help to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the EAI solution is delivering the expected benefits to the organization.
-
Foster Collaboration and Communication:
Create a work environment that fosters collaboration and facilitates open communication among IT teams, business units, and stakeholders involved in the integration project. This will help ensure that everyone is aligned, promote knowledge sharing, and facilitate faster issue resolution.
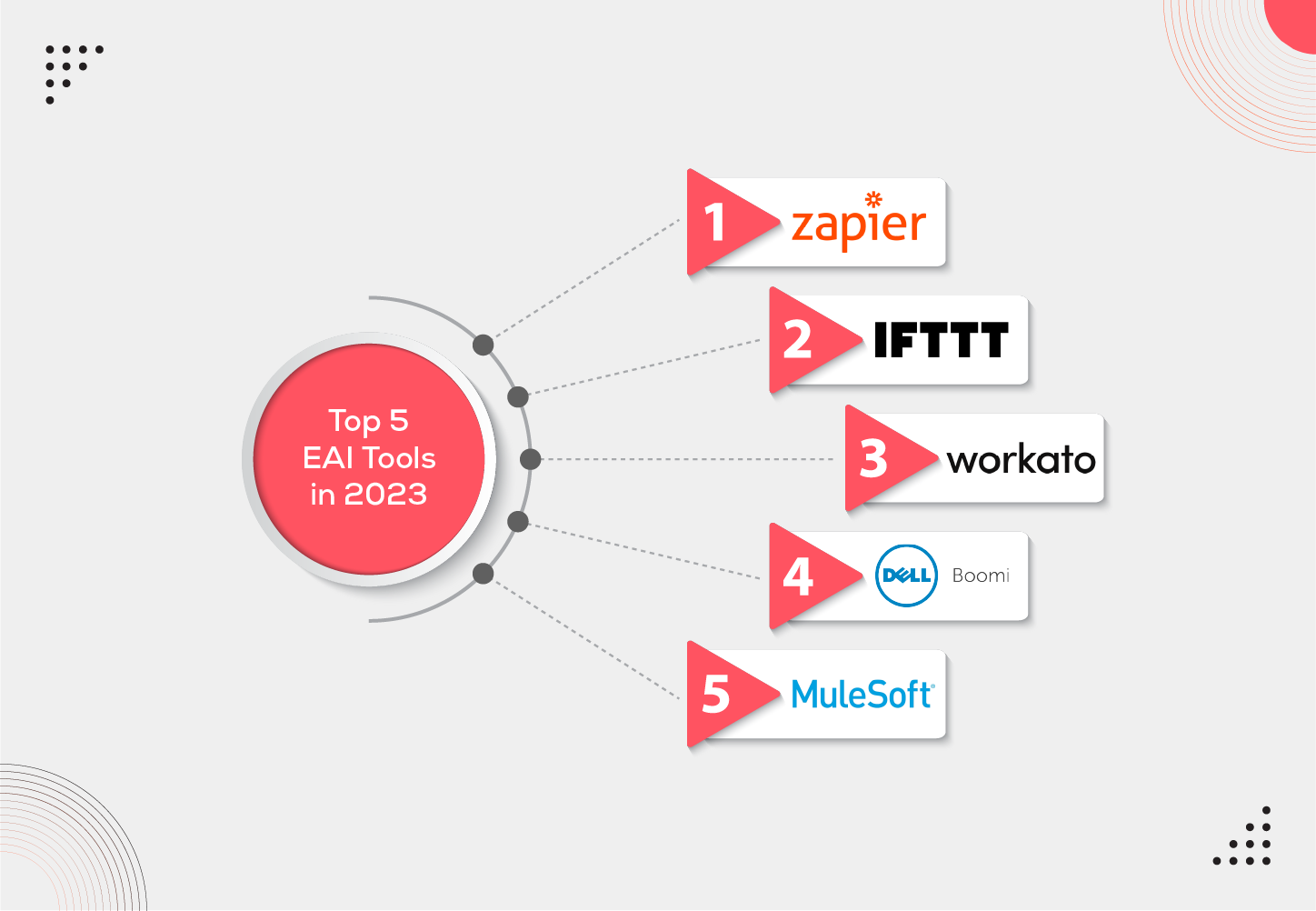
Top Five EAI Integrated Tools in 2023
Conclusion
There is no doubt in the fact that Enterprise Application Integration plays a vital role in connecting businesses digitally by breaking down data silos, synchronizing processes, and enabling seamless communication between applications. The only way to enhance operational efficiency, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in today's rapidly growing digital landscape is by implementing effective EAI strategies and leveraging integration technologies. Embracing Enterprise Application Integration is no longer just an option but a necessity for businesses looking to thrive in the interconnected world of the digital age.